Halui Examples
For any Halui examples to work you need to add the following line to the [HAL] section of the ini file.
HALUI = haluiRemote Start
To connect a remote program start button to Machinekit you use the
halui.program.run pin and the halui.mode.auto pin.
You have to insure that it is OK to run first by using the
halui.mode.is-auto pin. You do this with an and2
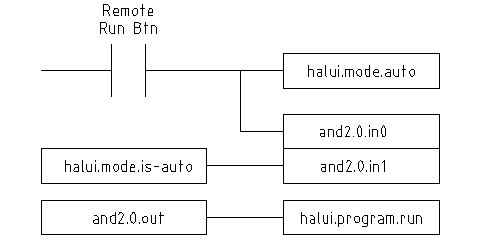
component. The following figure shows how this is done.
When the Remote Run Button is pressed it is connected to
both halui.mode.auto and and2.0.in0. If it is OK for
auto mode the pin halui.mode.is-auto will be on.
If both the inputs to the and2.0 component are on the
and2.0.out will be on and this will start the program.
The hal commands needed to accomplish the above are:
net program-start-btn halui.mode.auto and2.0.in0 <= <your input pin> net program-run-ok and2.0.in1 <= halui.mode.is-auto net remote-program-run halui.program.run <= and2.0.out
Notice on line one that there are two reader pins, this can also be split up to two lines like this:
net program-start-btn halui.mode.auto <= <your input pin> net program-start-btn and2.0.in0
Pause & Resume
This example was developed to allow Machinekit to move a rotary axis on a signal from an external machine. The coordination between the two systems will be provided by two Halui components:
-
halui.program.is-paused
-
halui.program.resume
In your customized hal file, add the following two lines that will be connected to your I/O to turn on the program pause or to resume when the external system wants Machinekit to continue.
net ispaused halui.program.is paused => "your output pin" net resume halui.program.resume <= "your input pin"
Your input and output pins are connected to the pins wired to the other controller. They may be parallel port pins or any other I/O pins that you have access to.
This system works in the following way. When an M0 is
encountered in your G-code, the halui.program.is-paused
signal goes true. This turns on your output pin so that
the external controller knows that Machinekit is paused.
To resume the Machinekit gcode program, when the external controller is ready it will make its output true. This will signal Machinekit that it should resume executing Gcode.
Difficulties in timing
-
The "resume" input return signal should not be longer than the time required to get the g-code running again.
-
The "is-paused" output should no longer be active by the time the "resume" signal ends.
These timing problems could be avoided by using ClassicLadder to activate the "is-paused" output via a monostable timer to deliver one narrow output pulse. The "resume" pulse could also be received via a monostable timer.
